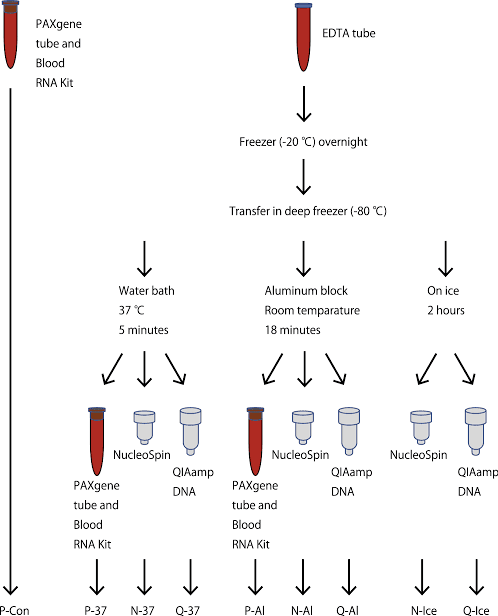
DNA extraction from whole blood is one of the most common and reliable methods used in molecular biology and genetics. It forms the foundation for many scientific and medical studies, including genetic testing, disease diagnosis, forensic analysis, and biomedical research. Extracting DNA from blood samples allows scientists and clinicians to analyze genetic material accurately, providing valuable insights into health, heredity, and cellular function.
DNA Extraction from Whole Blood – A Perfect Overview

What is DNA Extraction from Whole Blood?
DNA extraction from whole blood refers to the process of isolating pure deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from the blood cells of an organism. Blood is a rich source of DNA because it contains white blood cells (leukocytes), which have nuclei that store the genetic material. The goal of DNA extraction is to separate DNA from other cellular components such as proteins, lipids, and plasma. The result is a purified DNA sample that can be used for various molecular applications like PCR, sequencing, and genetic profiling.
Key Steps in DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
The process of DNA extraction from whole blood involves several important steps:
- Cell Lysis: The first step is breaking open the cells to release the DNA. This is done using lysis buffers containing detergents that dissolve cell membranes. White blood cells are targeted since red blood cells lack nuclei and therefore do not contain DNA.
- Protein Removal: Once the cells are lysed, proteins and other cellular debris are removed using enzymes like proteinase K or chemical reagents. This ensures that the final DNA is free from contamination.
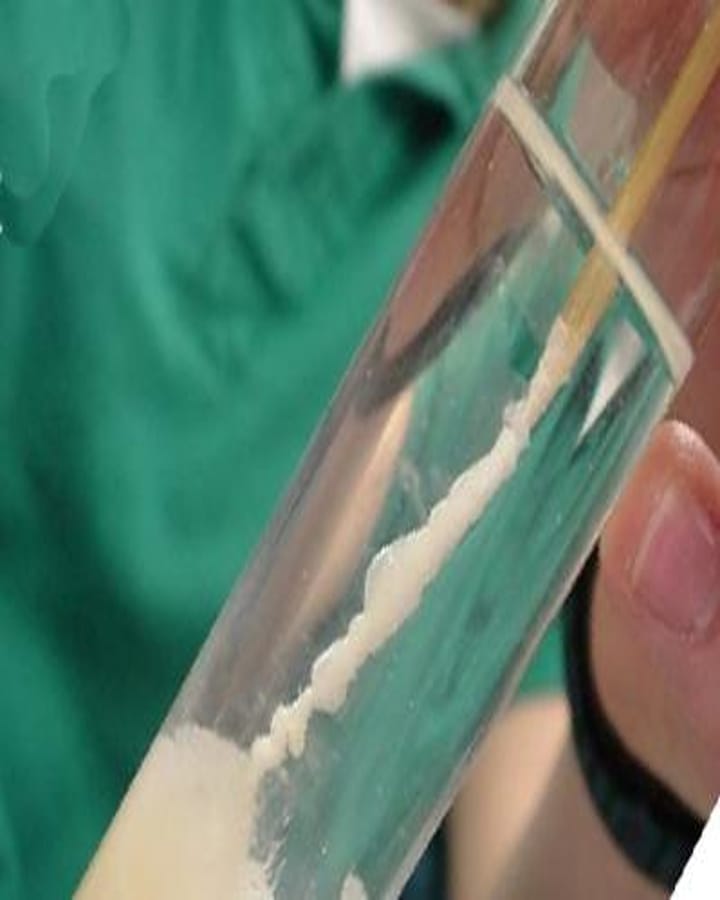
- DNA Precipitation: The DNA is then separated from the solution using alcohol, usually ethanol or isopropanol. When alcohol is added, DNA becomes visible as a white thread-like structure and can be collected easily.
- DNA Washing and Rehydration: The precipitated DNA is washed to remove any remaining impurities and then dissolved in a buffer solution or distilled water for storage and further use.
These steps may vary slightly depending on the extraction method—manual or automated—but the basic principles remain the same.
Methods Used in DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
There are several techniques for DNA extraction from whole blood, each with its own advantages:
- Phenol-Chloroform Extraction: A traditional method using organic solvents to purify DNA. It provides high-quality DNA but involves toxic chemicals.
- Silica Column-Based Kits: A popular method in modern laboratories. These kits use silica membranes that bind DNA selectively, allowing quick purification and high yield.
- Magnetic Bead-Based Extraction: This automated technique uses magnetic particles to bind DNA, making it suitable for high-throughput and clinical settings.
Choosing the right method depends on factors such as sample size, desired purity, cost, and laboratory setup.
Applications of DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
DNA extracted from blood samples has numerous applications across science and medicine:
- Genetic Testing: Identifying hereditary conditions and genetic mutations.
- Forensic Science: Matching DNA profiles for identification and criminal investigations.
- Medical Diagnostics: Detecting infectious diseases, cancers, and genetic disorders.
- Pharmacogenomics: Studying how genes influence a person’s response to medications.
- Research and Biotechnology: Used in cloning, sequencing, and gene expression studies.
Because blood samples are easy to collect and store, they are often the preferred source of DNA in both clinical and research environments.
Quality Control in DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
The success of DNA extraction depends on the purity and integrity of the isolated DNA. Factors such as sample handling, anticoagulants used (like EDTA or heparin), and storage temperature can affect the quality. Properly extracted DNA should be free from protein or chemical contaminants, with a high yield and suitable concentration for downstream applications.
DNA extraction from whole blood is a vital technique that supports advancements in genetics, medicine, and biotechnology. From diagnosing diseases to solving crimes, pure DNA obtained from blood serves as the foundation for countless scientific discoveries. Ensuring accuracy and quality at every step of extraction helps produce reliable results for research and clinical use.
Let us know in the comments if you’ve ever performed DNA extraction from whole blood or used DNA-based techniques in your lab—your experience can help others learn more about this essential process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is DNA extraction from whole blood?
DNA extraction from whole blood is the process of isolating pure DNA from white blood cells for genetic testing or research.
Which cells in blood are used for DNA extraction?
Which cells in blood are used for DNA extraction?
White blood cells are used for DNA extraction from whole blood because they contain nuclei with genetic material.
What are common methods for DNA extraction from whole blood?
The most common methods include phenol-chloroform extraction, silica column-based kits, and magnetic bead-based techniques.

